Inverse Square Law
By DarthVader
Date: 2025-11-23
Topic: 251 see comments
Post views: 35
Inverse Square Law
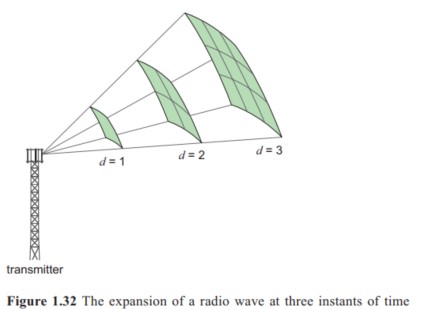
The inverse square law describes the reduction in power with distance from the transmitter, due to spreading.
It applies ideally to free space, where there is no other matter nearby to affect propagation.
P(d) = P0( \(\frac{d_0}{d}\) )2
P(d) = P0( (\frac{d_0}{d}\) )2
Where:
P(d) = received power at distance ‘d’
P0 = reference power measured at distance ‘d0’
d = distance from the transmitter
d0 = reference distance
Example:
If an antenna in free space receives 18 μW of power at a distance of 10 km from an isotropic transmitter, how much (in μW) will it receive at 20 km?
P(d) = 18 μW( \(\frac{10 km}{20 km}\) )2 = 4.5 μW
P(d) = 18 μW( (\frac{10}{20}\) )2 = 4.5 μW
| Comments | Creator | Date | ID |
|---|