Op Amps
By DarthVader
Date: 2024-11-15
Topic: 210 see comments
Post views: 300
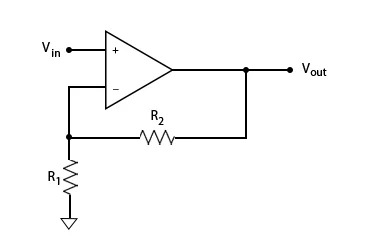
Non-inverting Op-amp (Image 1)
Gain = (Rf) / (R1) + 1
- Output signal is in phase with the input signal.
- The gain is always greater than or equal to 1.
- Suitable for high impedance sources (sensors or probes).
- Input impedance is very high, determined by the op-amps impedance.
- Commonly used in: Buffering (voltage followers), signal conditioning (sensors), audio amplification (phase preservation).
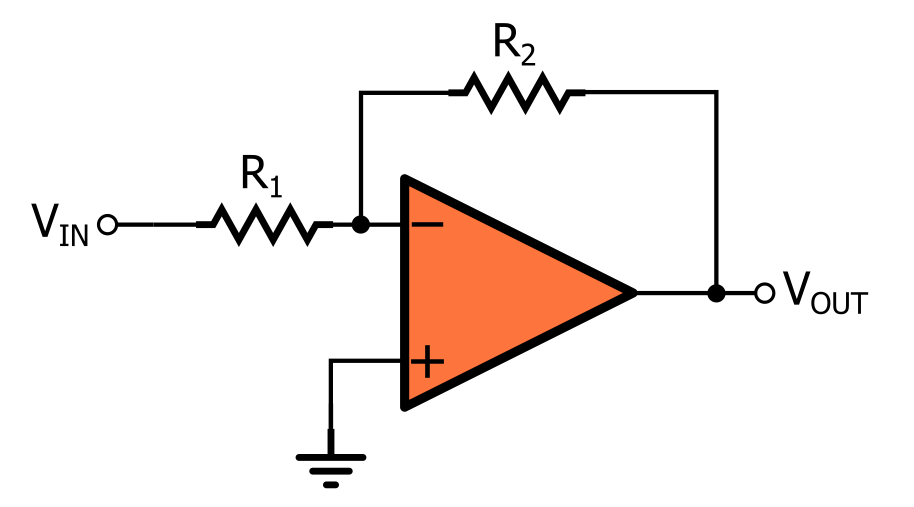
Inverting Op-amp (Image 2)
Gain = − (Rf) / (R1)
- Output signal is 180° out of phase with the input signal. (Inverted)
- The gain can be less than 1 or greater than 1.
- Input impedance can be very low.
- Commonly used in: Signal inversion
Open-Loop Op-amp (Comparator)
- If the non-inverting input (V+) is greater than the inverting input (V-), the output is equal to the positive supply voltage.
- If the inverting input (V-) is greater than the non-inverting input (V+), then the output is equal to the negative supply voltage.
| Comments | Creator | Date | ID |
|---|