BJT Transistors
By DarthVader
Date: 2025-05-18
Topic: 237 see comments
Post views: 195
Transistor types:
BJT Transistors:
- Note that BJT transistors always require a current limiting resistor connected to their base.
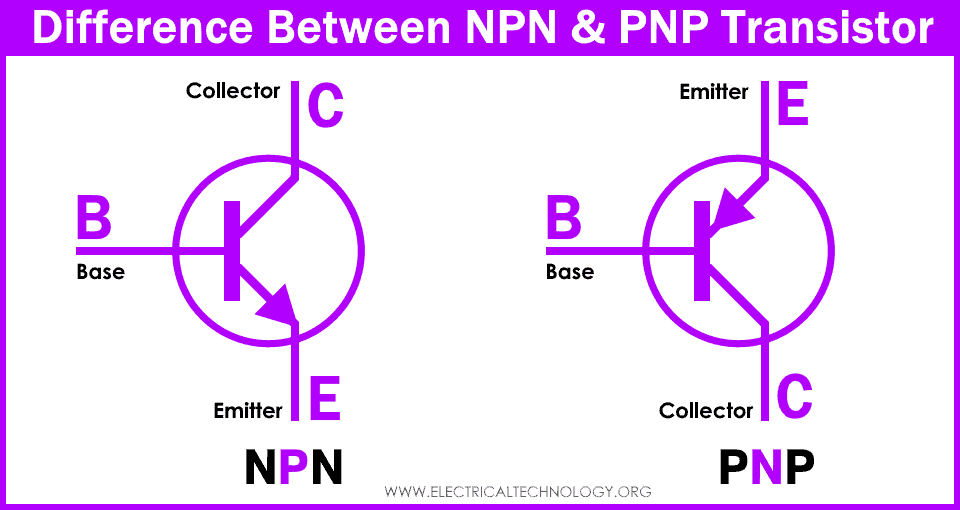
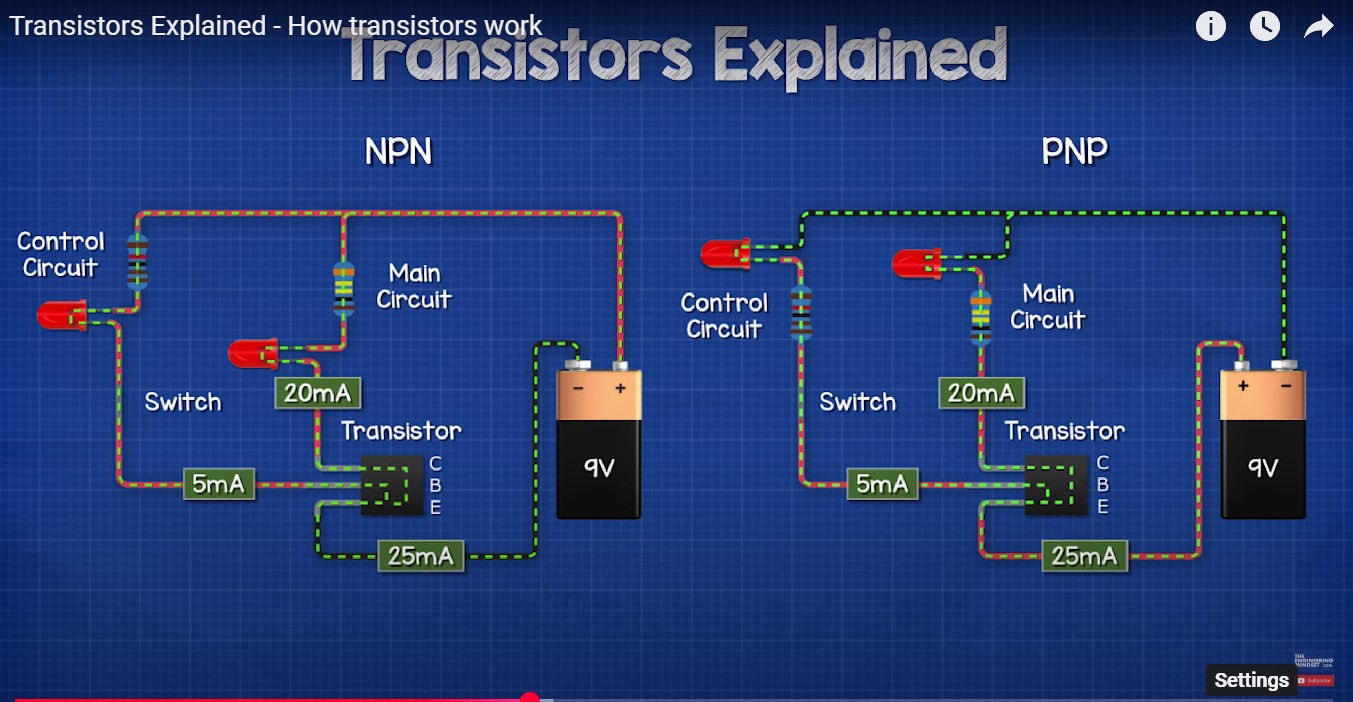
NPN
- When a small current flows into the base, a larger current flows from the collector to the emitter.
- To turn on, the base voltage must be more positive relative to the emitter (typically around +0.7V for silicon).
- Supply Voltage ⇢ Load ⇢ Collector ⇢ Emitter ⇢ Ground
PNP
- When a small current flows into the base, a larger current flows from the emitter to the collector.
- To turn on, the base voltage must be more negative relative to the emitter (typically around -0.7V for silicon).
- Supply Voltage ⇢ Emitter ⇢ Collector ⇢ Load ⇢ Ground
Choosing a base resistor:
1. Determine the collector current IC:
- Before you calculate the base resistor you need to know the desired output (collector) current IC
- This is determined by the current required by the load the transistor will be driving such as a relay, LED, motor, etc…
2. Determine the desired base current IB:
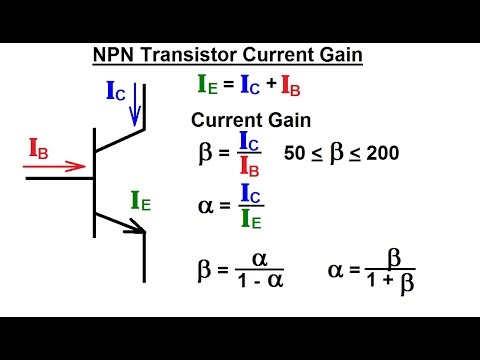
- Base current is related to output (collector) current by the transistors current gain. For an NPN transistor this is:
IC = β × IB
3. Calculate the base resistor RB:
Once you know the required base current, you can calculate the base resistor using Ohm’s law.
For NPN transistors:
RB = \(\frac{V_{drive}−V_{BE}}{I_{B}}\)
RB = \ (\frac{V_{drive}−V_{BE}}{I_{B}}\)
For PNP transistors:
RB = \(\frac{V_{CC}−V_{EB}−V_{drive}}{I_{B}}\)
RB = \ (\frac{V_{CC}−V_{EB}−V_{drive}}{I_{B}}\)
Where:
VCC = Supply voltage
Vdrive = Input voltage that drives the base
VBE(sat) = VB − VE (typically around 0.7 V for a silicon transistor)
VEB(sat) = VE − VB (typically around 0.7 V for a silicon transistor)
IB = Desired base current
Find the current gain:
(Note: this formula only works in the linear region not when the transistor is saturated)
β = \(\frac{I_{C}}{I_{B}}\)
β = \ (\frac{I_{C}}{I_{B}}\)
| Comments | Creator | Date | ID |
|---|