DC Motor Types
By DarthVader
Date: 2025-05-19
Topic: 239 see comments
Post views: 181
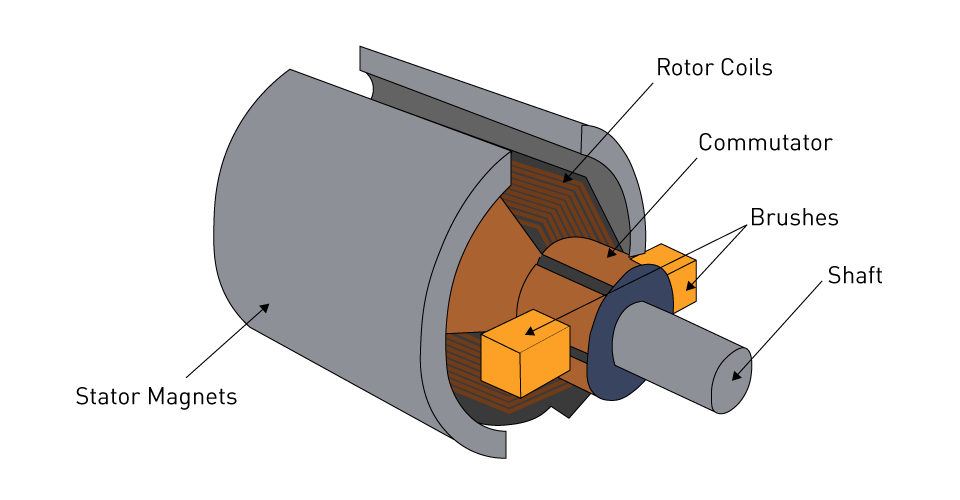
Conventional DC motors with an iron armature:
Contains: [ Rotor, Rotor coils, Stator/Stator magnets, Commutator and brushes. ]
| Advantages: | Disadvantages: |
High starting torque
| Lower efficiency (Lower efficiency than brushless or induction motors) |
Simple speed control (Easily controlled by adjusting voltage and current) | Maintenance requirements (Replacing/cleaning brushes and commutator) |
Low cost
| Bulky construction (Iron armatures) |
Reliable and durable
| Increased complexity (Brushes/commutator) |
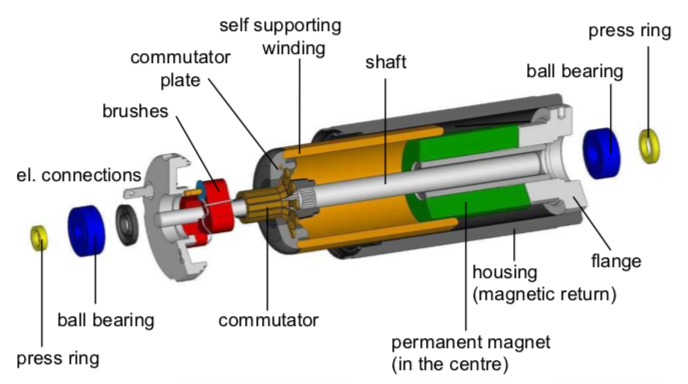
Ironless DC motors:
Contains: [ Ironless rotor made entirely of windings, Permanent magnet core, Outer casing ]
| Advantages: | Disadvantages: |
High efficiency
| Higher cost
|
Low inertia (Faster acceleration and deceleration) | Limited overload handling (No iron core for heat dissipation) |
Reduced noise and vibration
| Potential for overheating
|
Longer brush life
| Need for additional electronics (For control and operation) |
Better speed vs. torque characteristics (Linear speed-torque relationship) | Brush wear (While reduced, brush wear can still occur, requiring eventual replacement) |
Smaller size and weight
|
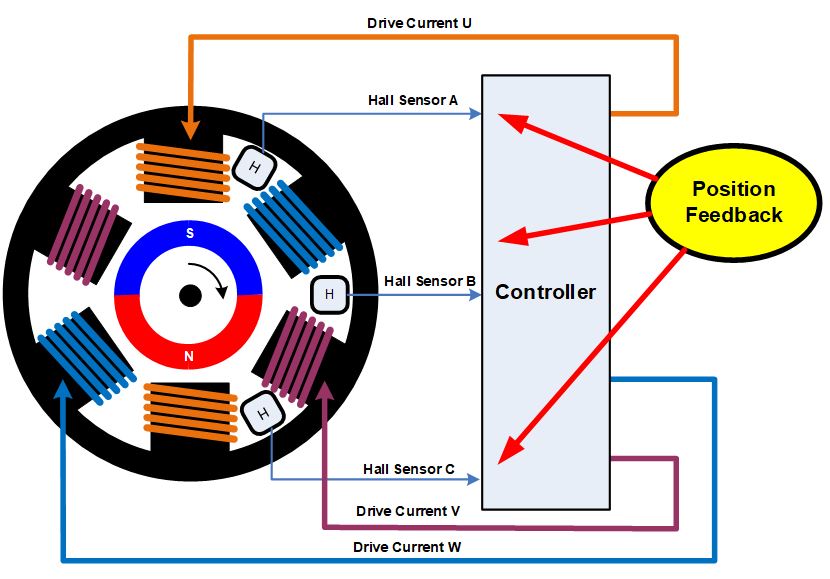
stepper motors:
Contains: [ Permanent magnets/Iron core, Multiple outer poles ]
| Advantages: | Disadvantages: |
High precision and accuracy (Suitable for applications requiring controlled movements) | Noisy at higher speeds
|
Easy to control (Easy to control using digital signals) | Less efficient at high speeds
|
Long lifespan
| Power consumption when holding position (They consume power even when holding a fixed position) |
Good torque at low speeds (They offer good torque, especially at low speeds, which is advantageous for applications requiring holding position or slow, precise movements) | Can miss steps (If the load torque is too high, a stepper motor may miss a step, affecting accuracy) |
Minimal maintenance
| Limited speed
|
| Comments | Creator | Date | ID |
|---|